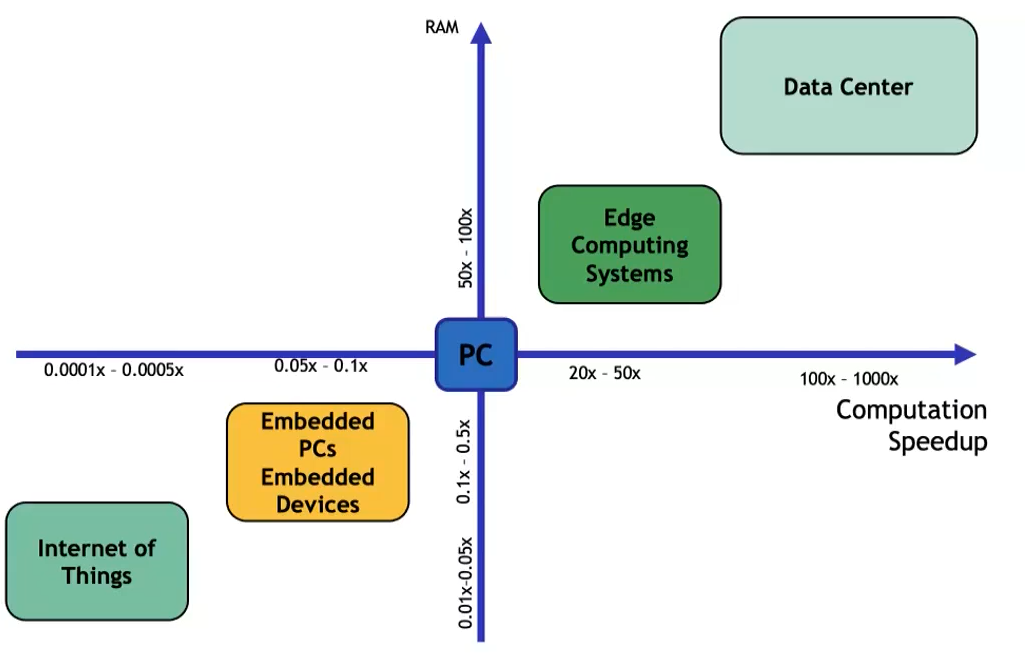
Data centers
Traditional data centers
The data center approach gained popularity in computing. DCs shift has led to the rise of Software as a Service (SaaS) and its widespread use. DCs also allow for more efficient and cost-effective execution of computationally intensive tasks, like training neural networks.
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|
| Lower IT costs | Require a constant Internet connection (so not work well with low-speed connections and latency problem) |
| High performance, “unlimited” storage capacity and backup | Privacy and security issues |
| Device independence (no need to manually configure …) | High Power Consumption |
Warehouse-scale Computer
From a DCs are moving towards Warehouse Scale Computers (WSCs). Actually WSCs can be considered as a type of DCs, the main concept is that:
- DCs consist of a collection of different servers
- WSCs use a relatively homogeneous hardware and system software platform to simplify management and reduce cost.
The machine is itself this large cluster or aggregation of servers and needs to be considered as a single computing unit.
Here the main differences:
- Traditional data centers:
- DCs usually house many small- or medium-sized applications.
- Each application runs on dedicated hardware, isolated from other systems.
- Applications within a data center typically do not communicate with each other.
- Data centers can host hardware and software for multiple organizational units or companies.
- WSCs:
- WSCs run few large applications or internet services
- There is a common resource management infrastructure which provides deployment flexibility
- The main requirements are homogeneity, single-organization control, and cost efficiency.