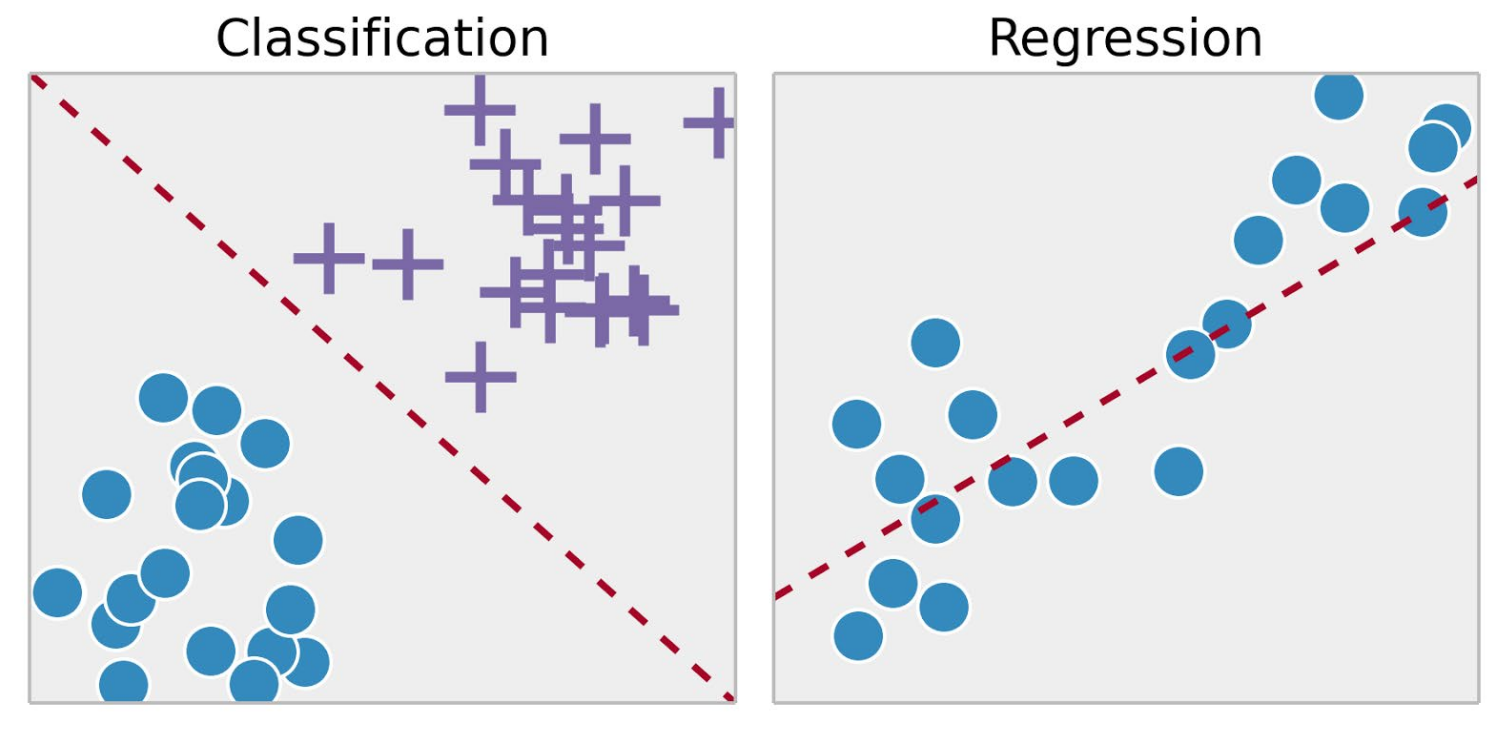
Supervised Learning
It is the most popular and well established learning paradigm. The goal is to learn a good approximation of an unknown function that maps an input to an output with:
- Loss function: a function which says “how much is good the approximation (called ) of ?”
- Hypothesis space: a subset of the set of all possible function
Supervised learning can be used every time we can’t clearly explain which is this function. Why shouldn’t we know what this function looks like?
- human cannot perform the task (DNA analysis)
- human cannot explain a clear algorithm (medical image analysis)
- the task continues to change over time (stocks price prediction)
- the task is user-specific (recommender system)
Supervised Learning is divided into: